- Home
- INNOVATION
- Introducing IFSCC Research Awards
- Maintaining beautiful skin by the skin sensing the scent component!?
Maintaining beautiful skin by the skin sensing the scent component!?
Top award for oral presentation at the IFSCC Conference 2021, Cancun
“Skin beauty with gentle-touch-receptor Merkel cells - Restore your senses with a pleasant scent”
What was the discovery?
Discovery of a possible new approach to create beautiful, healthy skin with scent without touching!
To maintain beautiful, healthy skin, we use cosmetics for daily skin care or sometimes take supplements containing nutrients that are said to be beneficial to the skin. This research found a possible new approach to beautiful skin by having the skin sense a particular scent component to create a healthy skin condition rather than the use of cosmetics and supplements.
How was this discovery found?
Success in capturing the details of certain cells responsible for the tactile sense in the skin by a combination of advanced technologies
We normally feel a tactile sensation by touching something or being touched. Unlike the visual sensation with the eyes and the auditory sensation with ears, which are associated with specialist organs, receptors that detect tactile sensations are located in the skin, which cover the surface of the body. This research examined Merkel cells, which were thought to be responsible for detecting tactile sensations of the skin.
Merkel cells are tactile receptor cells found in the basal layer between the epidermis and dermis (Figure 1). When the skin touches something or is touched, the information is detected by the Merkel cells and transmitted through the nerves to the brain. Previous research by Shiseido found that nerve fibers connected to Merkel cells are related to the maintenance of the structure of the dermis associated with skin firmness and sagging and demonstrated a novel concept of Merkel cells being related to the aging of the skin (Figure 2).
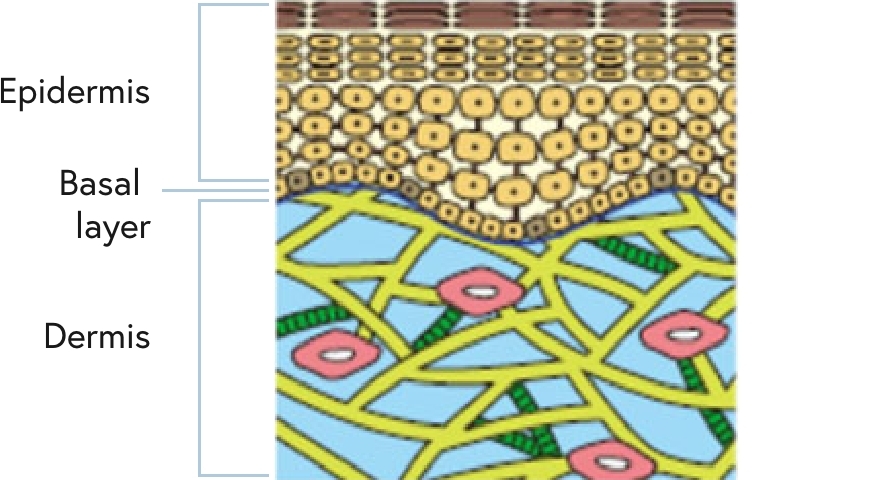
Figure 1
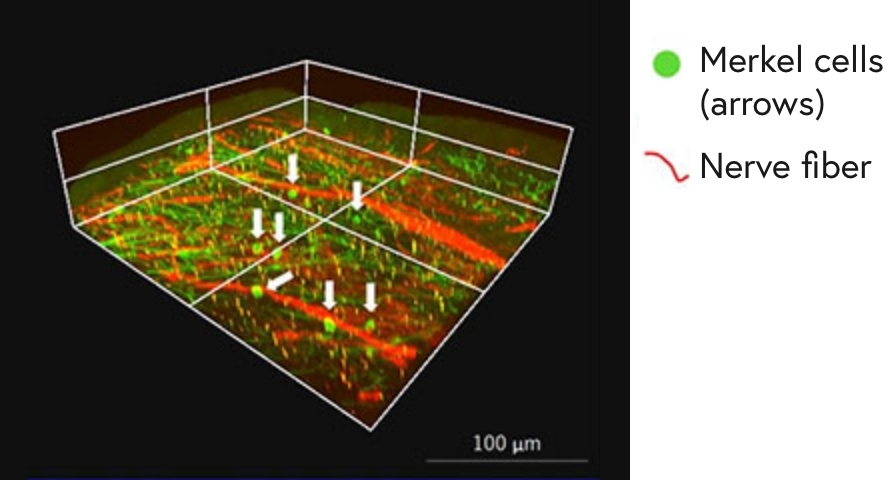
Figure 2:Merkel cells and nerve fibers observed under a multiphoton microscope
To observe these Merkel cells, the technology to exfoliate the epidermis from the skin and the 3D scanning technology using confocal microscopy were combined to successfully observe the distribution of Merkel cells in the skin tissue in detail. The result of the observation showed that the number of Merkel cells decreases with age in a similar manner to nerve fibers (Figure 3).
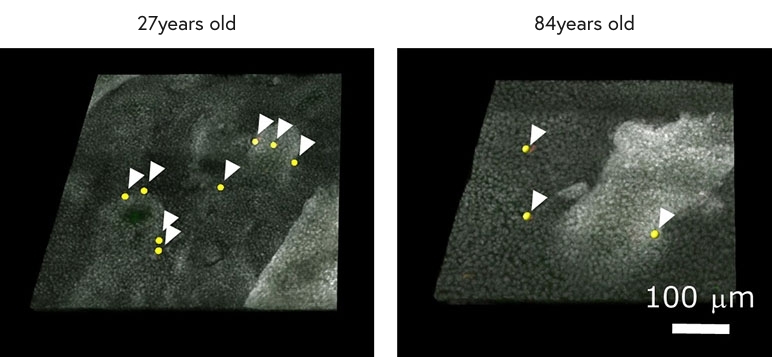
Figure 3:Decrease in Merkel cells with age. Merkel cells are shown with arrows.
Further observation of Merkel cells showed the expression of an odorant receptor in the Merkel cells, which are responsible for detecting scent components (Figure 4). Among the various scents, a sandalwood-like scent component is known to bind with this odorant receptor. When the solution containing sandalwood-like scent component was applied to human skin tissue, this was found to result in the activation of Merkel cells and release of NGF (nerve growth factor), which is known to help maintain healthy skin.
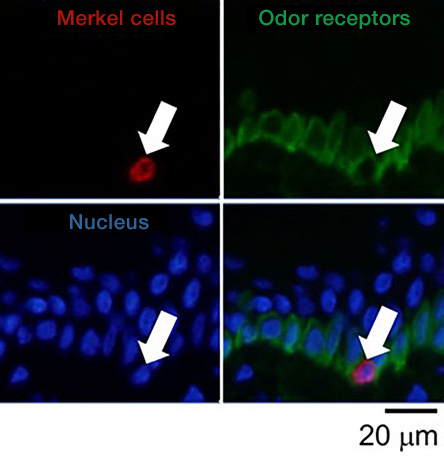
Figure 4:Expression of odor receptors (green) on the membrane of Merkel cells (red) (arrows)
This means that the detection of a sandalwood-like odor by Merkel cells will help maintain the skin in a beautiful and healthy condition, and it can be said to have expanded the possibility of a new beauty approach where Merkel cells, which were said to be activated by tactile sensation, are activated by scent components, allowing one to maintain healthy skin through both the application on the skin and the scent component. Shiseido will continue to conduct research on the relationship of the senses and nerves with the skin with the aim of realizing new beauty care.
Link to press release
ABOUT US
-
Who we are
-
History
-
Profile
-
Governance
-
Quality Management
-
Supply Network
-
Region/Business
BRANDS
-
Prestige
-
Premium
-
Inner Beauty
-
Life Quality Makeup
SUSTAINABILITY
-
Strategy / Management
-
Society
-
Environment
-
Governance
-
Reports / Data
-
Related Information
INNOVATION
-
Research and Development
-
Research Areas
-
Research outcomes
-
Product safety
-
Product Development Policy
-
Initiatives for doctors and researchers
CAREERS
-
DISCOVER OUR WORLD OF OPPORTUNITY
- Shiseido careers
INVESTORS
-
IR Library